What Contributes to Hormonal Imbalances?
Hormones don’t operate in a vacuum, and in some cases, it can be hard to pinpoint what’s caused by hormones and what’s caused by lifestyle choices. Factors such as stress, diet, activity levels, and sleep quality can also directly contribute to imbalances.
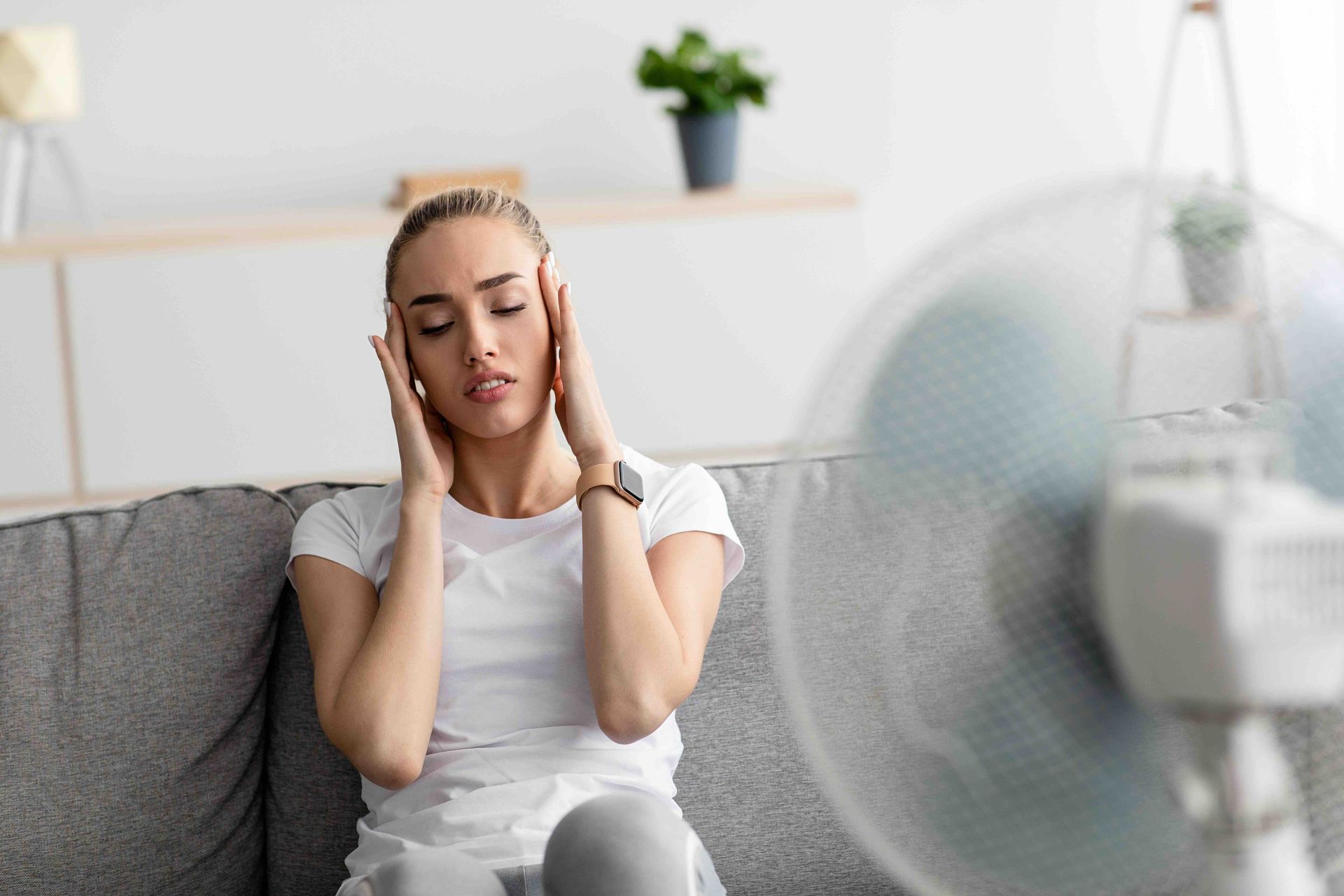
Chronic Stress
Chronic stress is one of the most significant
contributors to hormonal imbalances. When you experience stress, your body releases stress hormones like cortisol, which is designed to help you cope with immediate challenges.
However, if stress is prolonged, your body may continuously produce elevated levels of cortisol. Over time, this can disrupt the delicate balance of other hormones, such as estrogen, progesterone, and thyroid hormones.
Elevated cortisol can lead to symptoms such as weight gain, especially around the abdomen, trouble sleeping, mood swings, and even menstrual irregularities.
Prolonged stress can also
impact the adrenal glands, which are responsible for producing cortisol. As the adrenal glands become overworked, it can lead to adrenal fatigue, a condition where your body struggles to regulate cortisol and other hormones effectively.
This imbalance can contribute to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and feeling overwhelmed. Managing stress through mindfulness, relaxation techniques, or counseling can help restore hormonal balance and promote overall well-being.
Poor Diet
You’ve heard that you are what you eat, and that’s true for your hormone health, too.
A poor diet can significantly affect hormone levels and contribute to imbalances. Diets that are high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats can negatively impact insulin levels, gut health, and hormone production.
Excessive sugar intake can be especially concerning, according to
2022 research published in the Frontier of Immunology. Ingesting too many sweet treats can lead to insulin resistance, which in turn affects other hormones like estrogen and testosterone.
Additionally, a diet lacking essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats can hinder the body's ability to produce hormones efficiently.
Certain foods are particularly important for supporting hormone health. For example, omega-3 fatty acids, found in foods like salmon and flaxseeds, can help regulate inflammation and support healthy hormone production.
Similarly, foods rich in fiber, such as vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can help maintain balanced estrogen levels by supporting the body's detoxification process. A nutrient-dense diet can play a significant role in preventing hormonal imbalances and supporting overall well-being.
Lack of Sleep
Sleep plays an enormous role in regulating hormone levels. When you don’t get enough sleep, your body’s production of certain hormones, such as cortisol and growth hormone, can become disrupted (per the
Cleveland Clinic).
Cortisol levels tend to rise when sleep is inadequate, which can lead to a cycle of stress and fatigue. Inadequate sleep can also impact hunger-regulating hormones, such as ghrelin and leptin, leading to increased appetite and cravings for unhealthy foods.
Over time, this can contribute to weight gain and exacerbate other symptoms of hormonal imbalance.
Chronic sleep deprivation can also interfere with the production of estrogen and progesterone, two key hormones involved in the menstrual cycle and reproductive health. Inconsistent sleep patterns, especially over extended periods, can lead to irregular periods, mood changes, and even a reduced ability to conceive.
Prioritizing quality sleep—by establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a calm bedtime routine, and reducing screen time before bed—can help maintain hormonal balance and improve overall health.